Intracranial subdural haematomas: a rare but disabling complication of spinal anaesthesia
Main Article Content
Abstract
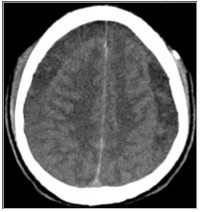
Background: Intracranial subdural haematomas (SDH) after subarachnoid blocks (SAB) are a very rare complication, which results in persistence of post procedure headaches and neurologic deterioration. Acute change in CSF pressure dynamics resulting in tears of bridging veins has been implicated.
Aim: To highlight our findings of intracranial SDH following SAB in the period 2018 to 2023 in Port Harcourt.
Methods: Patients who had persistent headaches with neurologic deterioration after SAB had brain imaging done. Those with SDH were recruited. They had burr hole evacuation of haematomas.
Results: Twelve patients (11 females), with a mean age of 41.0±9.8 years were recruited. Ten patients had SAB, and 2 had Combined spinal epidural (CSE) anaesthesia. SAB was done with size 22G spinal needle in 3 patients and 24G in 5 patients. Confusion, headaches, alteration in consciousness, and paresis occurred in 66.7%, 100%, 75% and 83.3% of patients respectively. 16.7% patients were Mark-Walder grade IV, 8.3% grade III, 41.7% grade II, and 33.3% with grade I. 41.7% patients had bilateral SDH and 33.3% had left SDH. Chronic SDH was noted in 41.7% patients and others had subacute SDH. Mean interval between onset of symptoms to surgery was 6.3±7.3 days. Clinical recoveries were noted in all patients with postoperative modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 14 days of 0.
Conclusion: Intracranial subdural haematomas may be rare but are a major cause of headaches with neurologic deteriorations after subarachnoid blocks. A high index of suspicion and prompt management results in good outcomes.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The journal grants the right to make small numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
References
1. Sule AZ, Isamade ES, Ekwempu CC. Spinal anaesthesia in lower abdominal and limb surgery: a review of 200 cases. Niger J Surg Res 2005;7(1-2):226-230.
2. Shui M, Zhao D, Xue Z, Wu A. Impact of spinal/epidural anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia on perioperative outcomes in patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Spine Surg 2023;36(6):227-236.
3. Adekola OO, Desalu I, Adekunle MO, Asiyanbi GK, Irurhe NK. Complications and outcomes following central neuraxial anaesthesia in a sub-Saharan tertiary hospital: the legal implication. Egypt J Anaesth 2015;31(2):189-195.
4. Pitkänen MT, Aromaa U, Cozanitis DA, Förster JG. Serious complications associated with spinal and epidural anaesthesia in Finland from 2000 to 2009. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2013;57(5):553-564.
5. Beck J, Gralla J, Fung C, Ulrich CT, Schucht P, Fichtner J, et al. Spinal cerebrospinal fluid leak as the cause of chronic subdural haematomas in nongeriatric patients. J Neurosurg 2014;121(6):1380-1387. (6 authors before et al.)
6. Acharya R, Chhabra SS, Ratra M, Sehgal AD. Cranial subdural haematoma after spinal anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2001;86(6):893-895.
7. Yildirim GB, Colakoglu S, Atakan TY, Büyükkirli H. Intracranial subdural haematoma after spinal anaesthesia. Int J Obstet Anesth 2005;14(2):159-162.
8. Kelsaka E, Sarihasan B, Baris S, Tur A. Subdural haematoma as a late complication of spinal anaesthesia. J Neurosurg Anaesthesiol 2003 ;15(1):47-49.
9. Turnbull DK, Shepherd DB. Post‐dural puncture headache: pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Br J Anaesth 2003;91(5):718-729.
10. Bezov D, Lipton RB, Ashina S. Post‐dural puncture headache: part I diagnosis, epidemiology, aetiology, and pathophysiology. Headache 2010;50(7):1144-1152.
11. Machurot PY, Vergnion M, Fraipont V, Bonhomme V, Damas F. Intracranial subdural haematoma following spinal anaesthesia: case report and review of the literature. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg 2010; 61(2):63–66.
12. Amorim JA, Remígio DS, Damázio Filho O, Barros MA, Carvalho VN, Valença MM. Intracranial subdural haematoma post-spinal anaesthesia: report of two cases and review of 33 cases in the literature. Rev Bras Anaestesiol 2010;60(6):624-629.
13. Bekele D, Bayable M, Bedane A. Chronic subdural haematoma after spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2021;15(1):492.
14. Moore AR, Wieczorek PM, Carvalho JCA. Association between post–dural puncture headache after neuraxial anaesthesia in childbirth and intracranial subdural haematoma. JAMA Neurol 2020; 77(1):65–72.
15. Maranhao B, Liu M, Palanisamy A, Monks DT, Singh PM. The association between post‐dural puncture headache and needle type during spinal anaesthesia: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Anaesthesia 2021;76(8):1098-1110.
16. Bjarnhall M, Ekseth K, Boström S, Vegfors M. Intracranial subdural haematoma: a rare complication following spinal anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1996; 40(10):1249–1251.
17. Cohen JE, Godes J, Morales B. Postpartum bilateral subdural haematomas following spinal anaesthesia: case report. Surg Neurol 1997; 47(1):6–8.
18. Cuypers V, van de Velde M, Devroe S. Intracranial subdural haematoma following neuraxial anaesthesia in the obstetric population: a literature review with analysis of 56 reported cases. Int J Obstet Anaesth 2016; 25: 58–65.
19. Szeto V, Kosirog J, Eilbert W. Intracranial subdural haematoma after epidural anaesthesia: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Emerg Med 2018;11(1):36.
20. Feghali J, Yang W, Huang J. Updates in chronic subdural haematoma: epidemiology, aetiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and outcome. World Neurosurg 2020; 141:339-345.
21. Shlobin NA, Kedda J, Wishart D, Garcia RM, Rosseau G. Surgical management of chronic subdural haematoma in older adults: a systematic review. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2021;76(8):1454-1462.
22. Macon ME, Armstrong L, Brown EM. Subdural haematoma following spinal anaesthesia. Anesthesiology 1990;72(2):380-381.
23. Bos EM, van der Lee K, Haumann J, de Quelerij M, Vandertop WP, Kalkman CJ, et al. Intracranial haematoma and abscess after neuraxial analgesia and anaesthesia: a review of the literature describing 297 cases. Reg Anaesth Pain Med 2021;46(4):337-343.
24. Flaaten H, Rodt SA, Vamnes J, Rosland J, Wisborg T, Koller ME. Postdural headaches: a comparison between 26-29G needles in young patients. Anaesthesia 1989;44(2) :147-149.
25. Halpern S, Preston R. Postdural puncture headache and spinal needle design. Metaanalyses. Anaesthesiology 1994;81(6):1376-1383.
26. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004; 24 Suppl 1:9–160.
27. Puig J, Shankar J, Liebeskind D, Terceño M, Nael K, Demchuk AM, et al. From “time is brain” to “imaging is brain”: a paradigm shift in the management of acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging 2020;30(5):562-571.
28. Parizel P, Makkat S, Van Miert E, Van Goethem J, Van den Hauwe L, De Schepper A. Intracranial haemorrhage: principles of CT and MRI interpretation. Eur Radiol 2001;11(9):1770-1783.
29. Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW, et al. Surgical management of acute subdural haematomas. Neurosurgery 2006; 58(3 Suppl): S216–S224.
30. Zhang J, Jin D, Pan KH. Epidural blood patch for spontaneous intracranial hypotension with chronic subdural haematoma: a case report and literature review. J Int Med Res 2016;44(4): 976–981.
31. Girgis F, Shing M, Duplessis S. Thoracic epidural blood patch for spontaneous intracranial hypotension: case report and review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg 2015; 25(2):320–325.
32. Okada Y, Akai T, Okamoto K, Iida T, Takata H, Iizuka H. A comparative study of the treatment of chronic subdural haematoma—burr hole drainage versus burr hole irrigation. Surg Neurol 2002;57(6):405-409.
33. Han HJ, Park CW, Kim EY, Yoo CJ, Kim YB, Kim WK. One vs. two burr hole craniostomy in surgical treatment of chronic subdural haematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2009;46(2):87-92.
34. Markwalder TM, Steinsiepe KF, Rohner M, Reichenbach W, Markwalder H. The course of chronic subdural haematomas after burr-hole craniostomy and closed-system drainage. J Neurosurg 1981;55(3):390-396.